Expert Tips on Designing Tailored Wastewater Management Plans
Expert Tips on Designing Tailored Wastewater Management Plans
Blog Article
Comprehending Wastewater Therapy Processes and Their Environmental Effect
The intricacies of wastewater therapy procedures play a critical function in mitigating ecological challenges linked with water pollution. Each stage, from initial to advanced treatments, is made to deal with certain impurities, eventually guarding both public health and water ecosystems. Nevertheless, despite technical advancements in treatment performance, significant difficulties linger, including the administration of recurring pollutants and the ramifications of nutrient drainage. As we discover the complexities of these procedures, it comes to be important to wonder about how much existing techniques can evolve to satisfy the growing demands of sustainability and ecological conservation.
Review of Wastewater Therapy
Exactly how is wastewater transformed right into a secure resource for the environment? Wastewater therapy is a critical procedure made to eliminate pollutants from used water, therefore safeguarding public wellness and safeguarding communities. This process starts with the collection of wastewater from property, industrial, and business resources, which is then directed to therapy facilities.
At these facilities, various physical, chemical, and organic approaches are utilized to deal with the wastewater. Preliminary screening removes large particles, followed by sedimentation to separate larger solids. Ultimately, biological therapies, such as triggered sludge procedures, utilize microbes to break down natural matter. These approaches not only minimize pollutant levels yet also promote the healing of beneficial nutrients.
The treated effluent can be securely released into natural water bodies or recycled for irrigation and industrial objectives, promoting resource preservation. Additionally, the therapy procedure generates biosolids, which can be repurposed as plant foods or dirt amendments, additionally boosting sustainability.
Stages of Treatment Procedures
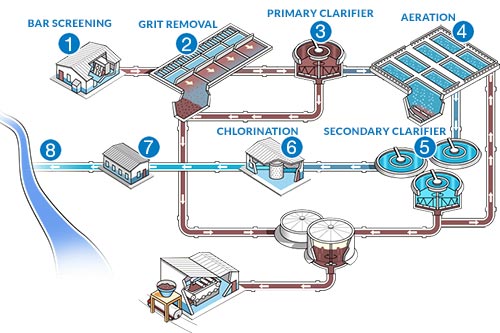
The wastewater treatment process generally is composed of 3 primary stages: preliminary, key, and secondary treatment. Each stage serves a distinctive duty in decreasing the contaminant lots and guaranteeing the effluent fulfills ecological standards before discharge.
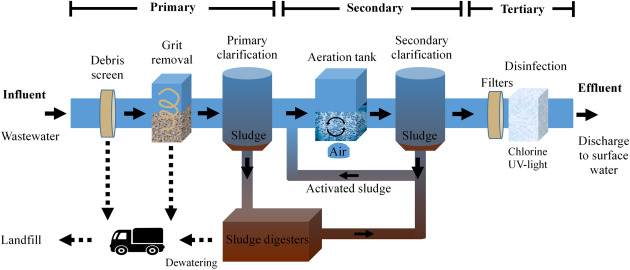
The key treatment stage concentrates on the physical splitting up of put on hold solids from the wastewater. Via sedimentation, heavier particles clear up at the end of sedimentation containers, forming sludge, while lighter materials, such as oils and greases, float to the surface area and are skimmed. This procedure significantly decreases the natural and inorganic load in the wastewater.
Additional therapy is an organic process targeted at additional minimizing the focus of natural issue. Numerous methods, consisting of turned on sludge systems and trickling filters, utilize microorganisms to metabolize natural contaminants. This stage is important for accomplishing the required biochemical oxygen need (BODY) reduction, ultimately leading to cleaner effluent ready for discharge or more therapy. Each stage is important in safeguarding ecological and public wellness.

Advanced Treatment Technologies
Adhering to the additional therapy processes, progressed treatment innovations play a vital function in more boosting the top quality of treated wastewater. These innovations are made to remove recurring contaminants that are not successfully removed during main and second treatments, making sure the effluent fulfills strict regulative criteria.
Among the commonly used innovative treatment techniques are membrane layer purification, reverse osmosis, and advanced oxidation processes. Membrane filtering, consisting of microfiltration and ultrafiltration, works in separating fine fragments, virus, and colloids from the water (Wastewater). Reverse Web Site osmosis utilizes semi-permeable membranes to eliminate liquified solids, leading to top quality water appropriate for different applications
Advanced oxidation procedures (AOPs) use strong oxidants to degrade organic contaminants, consisting of drugs and individual treatment items that are immune to standard therapy. These approaches boost the biodegradability of complex compounds, promoting their elimination.
An additional substantial technology is using biological nutrient removal processes, which specifically target nitrogen and phosphorus, avoiding eutrophication in getting water bodies. In general, sophisticated treatment innovations are vital for accomplishing higher levels of purification, advertising water reuse, and guarding public wellness while attending to the difficulties connected with wastewater administration.
Environmental Benefits of Therapy
Countless ecological benefits occur from effective wastewater treatment procedures that add to ecosystem wellness and sustainability. Largely, these procedures substantially minimize the release of hazardous toxins right into natural water bodies, which helps keep water ecological communities. By getting rid of pollutants such as heavy steels, nutrients, and microorganisms, treated wastewater minimizes the danger of waterborne diseases and advertises biodiversity in marine settings.
Additionally, wastewater treatment centers typically employ innovative innovations that enable this post water recycling and reuse. This technique not only preserves freshwater sources but additionally minimizes the demand on all-natural water materials. Boosted nutrient removal from wastewater can also stop eutrophication, a process that brings about algal flowers and succeeding oxygen exhaustion in marine systems.
Additionally, reliable treatment procedures can minimize greenhouse gas exhausts, particularly methane and laughing gas, which are frequently launched during neglected wastewater decay. By catching and utilizing biogas from anaerobic digesters, facilities can convert waste right into eco-friendly power, consequently adding to a reduction in nonrenewable fuel source dependency.
Challenges and Future Patterns
While the ecological benefits of wastewater treatment are clear, a number of obstacles persist that impede optimal outcomes in this field. One major concern is maturing infrastructure, which commonly leads to ineffectiveness and boosted functional prices - Wastewater. Many treatment plants were created years earlier, and their capacities do not align with modern demands, which consist of more stringent governing criteria and higher volumes of wastewater due to urbanization
Looking in advance, there is an expanding emphasis on source healing and circular economy concepts within wastewater treatment. Innovations such as anaerobic food digestion, which can produce biogas, and progressed purification innovations are gaining grip. These techniques not only boost therapy effectiveness but also advertise sustainability.
Eventually, dealing with these difficulties requires cooperation among stakeholders, investment in modern technology, and a dedication to ongoing research. By accepting these trends, the wastewater therapy industry can evolve to satisfy the demands of a transforming environment and culture.
Conclusion
In conclusion, wastewater treatment procedures play an important function in boosting ecological Extra resources quality and public health. The multi-stage therapy structure, coupled with advanced technologies, successfully minimizes pollution and promotes sustainable water administration.
Report this page